Experts recently published a study looking at artificial methods to cool the planet and combat the effects of climate change. This study claims to contradict some old fears about the impact of using such artificial measures.
However, many scientists are dubious about the study. They claim it’s not comprehensive enough and doesn’t properly consider the risks of the methods it advocates.
Geoengineering

Geoengineering basically describes the practice of employing emerging technologies to manipulate the environment. The aim of this manipulation is to offset some of the impacts of climate change.
Solar geoengineering specifically looks to reflect a small amount of sunlight into space or boost the amount of solar radiation that escapes back into space in an effort to cool the planet.
Concerns About Geoengineering

There are numerous concerns about the idea of geoengineering in this way, foremost among them being whether it’s safe.
Solar geoengineering to cool the planet would likely involve spraying sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere. It would mimic gas from volcanoes and reflect heat from the sun. Many scientists believe spraying sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere in this way might be unsafe.
The New Study

A study published in Nature Climate Change, a peer-reviewed journal, proposes a geoengineering climate change solution that resolves some of the potential problems associated with the practice.
The paper suggests that using geoengineering to cool the Earth to the point of eliminating roughly half of warming as opposed to all of it generally wouldn’t worsen things like water availability, extreme rain and extreme temperatures and wouldn’t make hurricanes more intense.
Researchers Still Acknowledge Some Risks

The study does acknowledge that artificially cooling the climate wouldn’t be totally without risk. The study states that a small fraction of places, 0.4%, may still see the impacts of climate change worsen.
Harvard Professor David Keith, co-author of the study, states, “I am not saying we know it works and we should do it now.” He adds, “Indeed, I would absolutely oppose deployment now. There’s still only a little group of people looking at this. There’s lots of uncertainty.”
Criticisms of the Paper

Some critics of the study say that advocates of the paper may be overstating the findings of the study.
Alan Robock of Rutgers University says that the paper doesn’t look closely enough at the specific methods that would be utilized to cool the planet artificially and the potential consequences of these methods.
Atmospheric Aerosols

According to Robock, a geophysics professor and researcher, the most likely method of turning down the heat of the sun would be through the use of aerosols sprayed into the atmosphere.
“They focus in this paper on temperature and water availability in different regions,” Robock said. “Those are only two things that would change with stratospheric aerosols.”
Risks of Relying on Unproven Technology

Some climate advocacy groups are concerned about relying on unproven technology to cool the climate, suggesting that doing so could hamper efforts to reduce carbon emissions from industry and vehicles.
Regardless, the technology itself could cost billions of dollars a year to implement after the research and development costs to get it viable.
Ethical Question

Robock claims other studies have similarly explored the notion of spraying atmospheric aerosols to cool the planet, saying one of his own studies lists 27 reasons why this approach may not be advisable.
Beyond this, Robock says there are ethical considerations to deploying the technology. “We’re not able right now to say whether, if global warming continues, we should ever decide to start spraying this stuff into the stratosphere,” Robock states. “Would solar-radiation management, would geoengineering make it more dangerous or less dangerous?”
The Intended Message of the Study

Critics of the study say it doesn’t explore specific techniques of solar geoengineering in enough detail to address potential dangers and determine whether the approach is viable or beneficial. But Harvard’s David Keith says this isn’t the point of the study.
Keith stated that the main message of the study is to not rule out geoengineering as a tool in fighting climate change, as “there is the possibility that solar geoengineering could really substantially reduce climate risks for the most vulnerable.”
May Be Necessary

Keith is not alone in recognizing that interventionist methods to try and artificially cool the planet might have to be explored in the future if the climate crisis worsens.
A U.N. report last year stated that using geoengineering via sulfur dioxide injected into the atmosphere may be necessary, though the approach comes with major uncertainties.
Artificially Manipulating Our Climate

As we continue to see the impacts of our planet’s changing climate, with increased extreme weather events all around the world year after year, it’s understandable that scientists are exploring every possible avenue to combat this change.
This includes potential technologies to artificially manipulate our climate. As these technologies are in their infancy, there is obviously pushback from some scientists about supporting their deployment too enthusiastically. But as the climate crisis worsens, expect to see the debate around geoengineering intensify.
Climate Emergency

Climate scientists, researchers, and activists are desperate to figure out a sustainable solution in the context of a lack of political will to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, but time is not on their side.
On Monday, activists held a “climate emergency day” that called for a “global day of action.”
Ticking Down
Demonstrators took to the streets to warn about the ticking clock on climate change that necessitates urgent action.
“The Climate Clock is ticking On July 22nd, let’s come together for #ClimateEmergencyDay. It’s #TimeToEndFossilFuels and #TimeToFundOurFuture. Share this post, join local actions and demand real climate solutions!” wrote the group Fossil Free California on X.
Climate Clock

An organization called Climate Clock helped organize the 2024 climate emergency day and keeps a running countdown clock on the time left to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celcius, which was an agreed-upon number to dampen the effects of climate change.
The worst consequences of climate change could theoretically be avoided if the temperature is kept from rising by no more than 1.5 degrees Celsius or 2.7 degrees Fahrenheit by the year 2100.
Less than Five Years
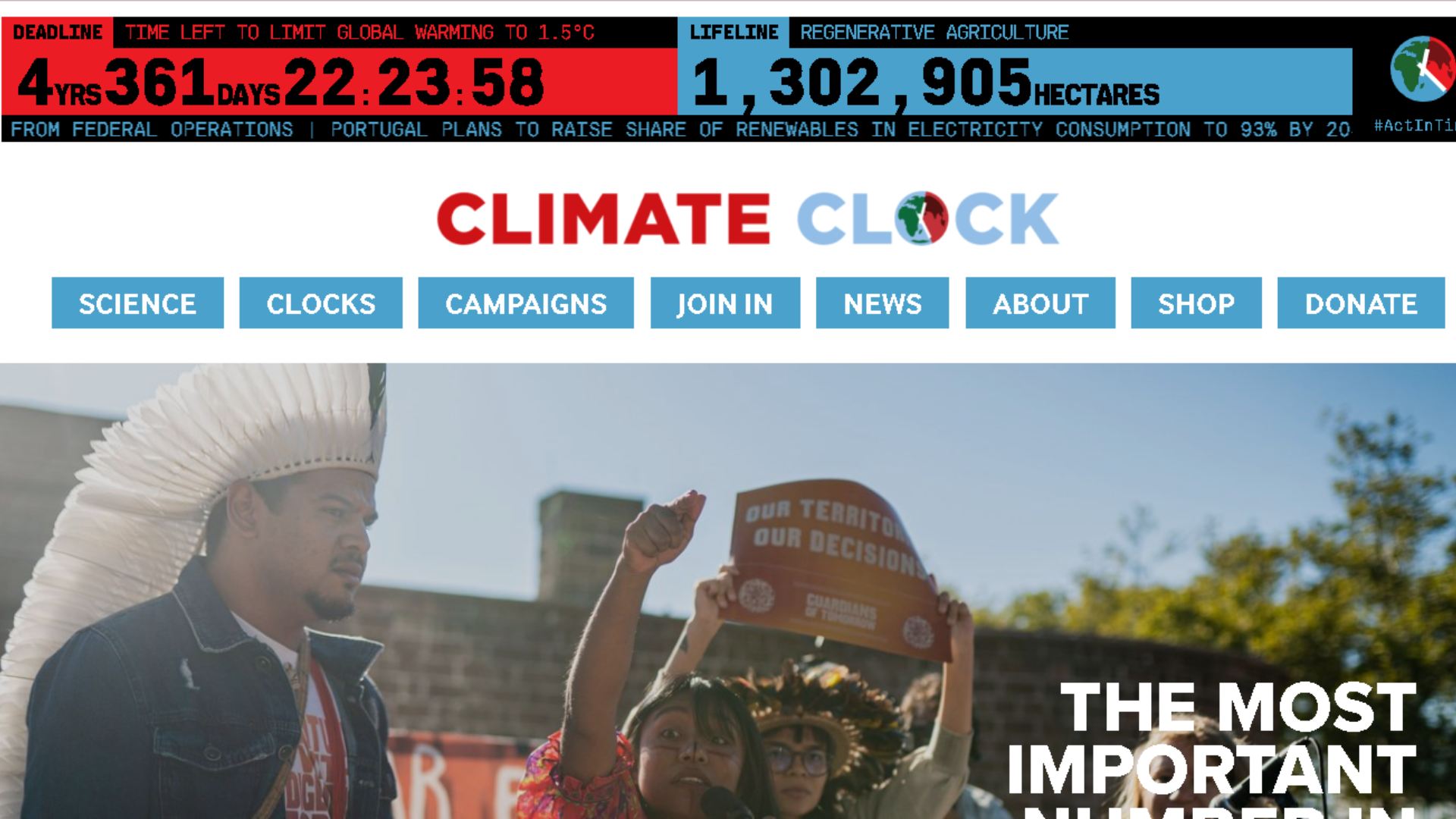
In a post supporting the climate emergency day, Climate Clock expressed worry at how far the clock has ticked down.
“On Monday July 22 2024, the Climate Clock will tick down below five years for the first time, a key milestone for humanity that will spark a wave of synchronised actions around the world, demanding an end to fossil fuels, and pushing leaders to #ActInTime to accelerate real climate solutions,” the post said.
1.5 Degrees

This temperature number was part of the 2015 Paris Climate Agreement, where 195 nations individually pledged to tackle climate change and keep global warming “well below” 2 degrees Celcius by 2100.
“One-point-five has become an iconic figure,” said Sir David King, former lead negotiator from the UK Foreign Office at the UN climate summit in Paris in 2015.
Can Geoengineering Help With This Goal?

According to Scientific American, techniques like solar geoengineering could keep global temperature increases under 1.5 degrees Celsius, but the problem is it’s not an ideal solution.
Governments would still need to come together to find ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the long-term or the problem would just be kicked down the road to a later time.
Not a Quick Fix

A 2023 study was critical of the idea of using geoengineering as a temporary stop-gap measure to help meet climate targets many across the world are pushing for.
The study found that solar geoengineering would have to be maintained for at least a century to keep global warming within the 1.5-degree threshold.
Something Bad Could Happen

Keeping up a solar geoengineering system for such a long time would require international cooperation and has its own risks.
“If we have to keep up a system like this for such a long time, that just increases the possibility of something bad happening,” said lead study author Susanne Baur, a doctoral candidate at the European Centre for Research and Advanced Training in Scientific Computation in France.
Can’t Rely on Geoengineering

Baur asserted that while geoengineering is marketed as a temporary solution, the data tells a different story.
“Geoengineering is “often communicated as temporary, a stopgap measure — so it implies being relatively short, and short in the sense of a couple of decades,” said Baur. “And so when we started looking at these pathways, and we extrapolated them a bit longer, we saw that in many cases, it’s actually not that short.”
Dangerous to Stop

Another major disadvantage of applying a solar geoengineering approach to fighting climate change is that once you start doing it you cannot easily stop without severe consequences.
A halt to geoengineering could cause skyrocketing temperatures which could be a shock to the system of plants and animals that they might not be able to recover from.
Potential for Side Effects
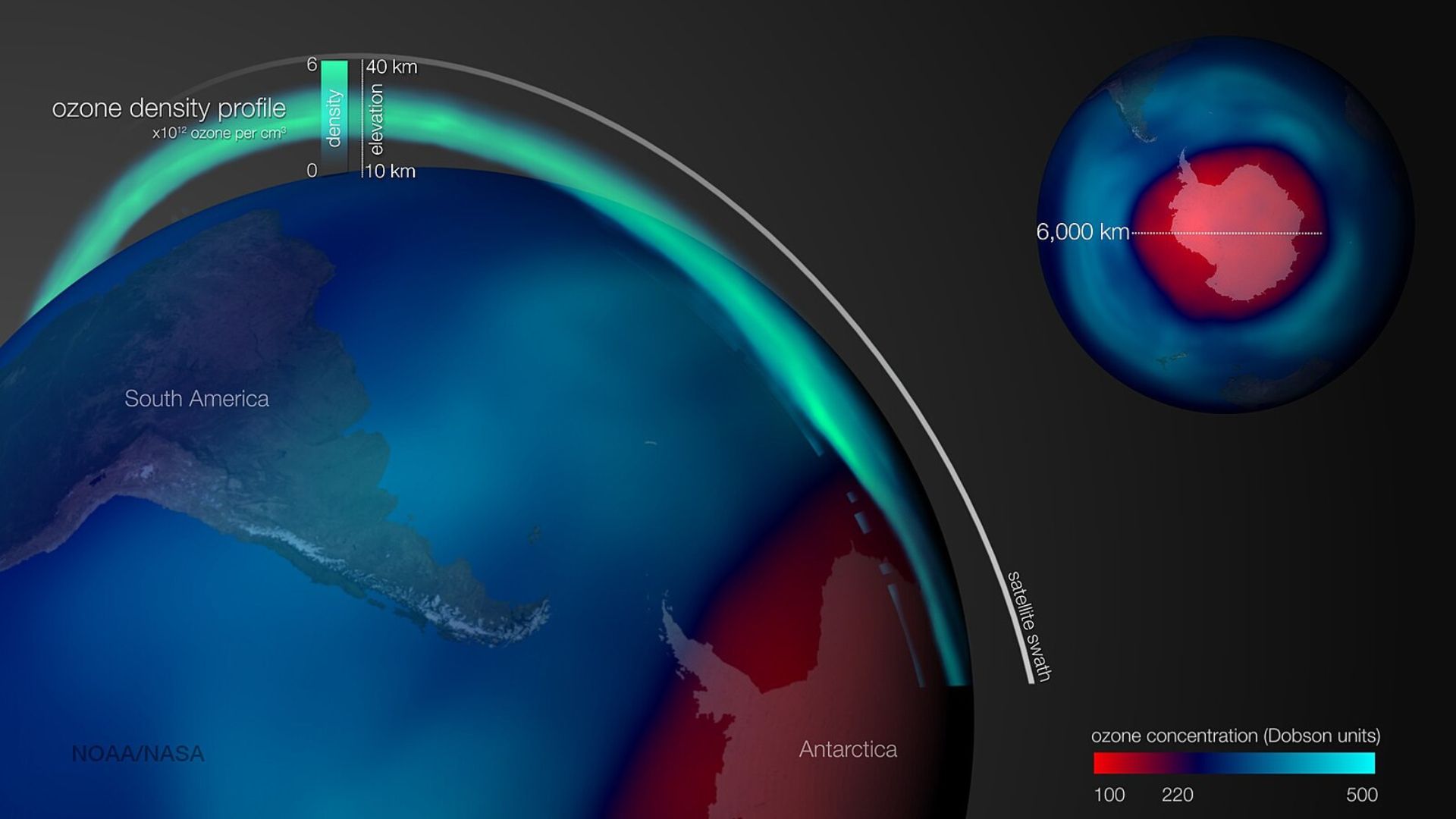
In addition to the risks of suddenly having to stop geoengineering, there are several side effects that the Earth will have to watch out for.
The possible use of aerosols may have the effect of causing a depletion in the ozone layer, an atmospheric layer that is responsible for protecting life on Earth from the dangers of radiation.
Oceans Become Acidic

Under a geoengineering climate plan, Earth’s oceans would continue to become more acidic as the excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is absorbed by the ocean.
This increased acidity would threaten habitats in the ocean and represent a threat to human health, making a plan to reduce carbon emissions essential to go with a geoengineering approach.
