Kenny’s Farmhouse Cheese has served everyone’s cheese needs for almost thirty years. However, the company has recently come under fire due to some cheese being recalled, which has resulted in fatal-warnings being issued.
Some of its cheese was found to have Listeria monocytogenes, a bacteria that can cause severe infections in those who consume it. Some people are more susceptible to these infections than others, and it’s important to know who these people are and what can be done about the cheese.
St. Jerome Cheese Recalled
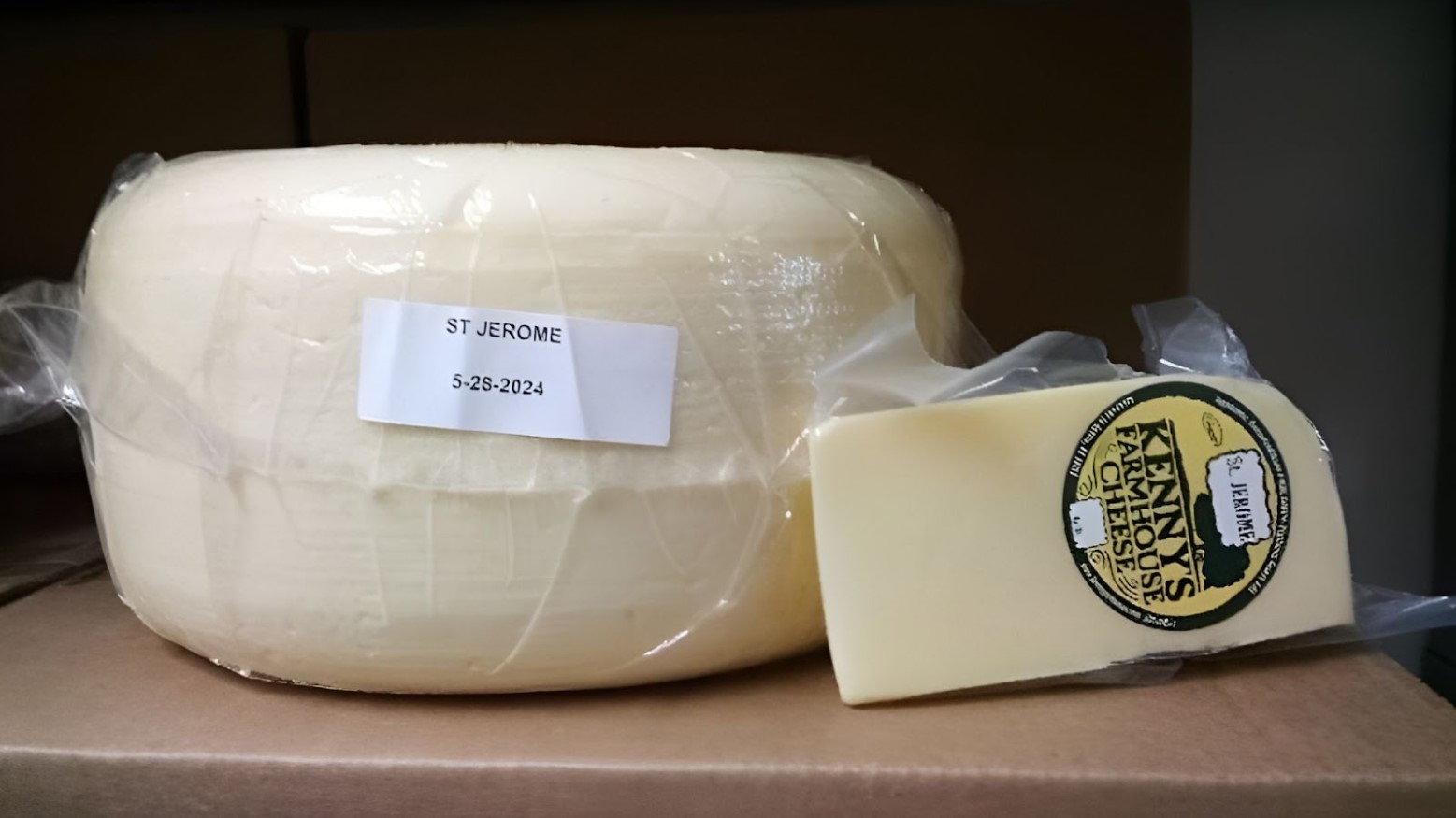

Only the St. Jerome cheese from Kenny’s Farmhouse Cheese has been recalled at this point. More specifically, batch 231129. It is important to note that none of its other cheeses have been recalled at the time of writing.
The cheese tends to be distributed from wholesale sellers, retail storefronts and the company’s website. It can be bought in two sizes: an 8-ounce wedge or a 15-pound wheel. The cheese is easily spotted as it is wrapped in clear plastic with a white label on the side.
Cheese Tested Positive for Listeria
The cheese was recalled due to it testing positive for Listeria. This was after routine testing found the bacteria, so the company decided to recall the batch of cheese before anyone became ill from it.
The Kentucky Department of Public Health carried out the routine testing. As part of the recall, customers have been urged to either return the cheese to where they bought it for a refund or throw it away. They have also been told not to consume any of it.
What Is Listeria?
Listeria is a type of bacteria that tends to cause food poisoning in those who consume food infected by it. While healthy individuals shouldn’t be too severely affected by it, pregnant women, people over the age of 65 and people with weakened immune systems are likely to suffer quite badly from it.
Listeria is mainly found in improperly processed deli meats and unpasteurized milk products. It can survive when put in the refrigerator or when frozen, and it is recommended that those at serious risk of infection avoid these products altogether.
Where Does Listeria Lurk?

Listeria monocytogenes, the technical classification for the disease-causing listeria bacteria, can be found in most moist environments.
This includes environments like soil, water, decaying animals and vegetation — a lot of environments that probably come to mind if you stop to think about what goes on in the food production industry.
Listeria Contamination

There are different stages of food production where conditions are perfect for these disease-causing bacteria to potentially infect food.
The listeria bacteria are typically transmitted when food is harvested, processed, prepared, packed, transported or stored in an environment contaminated with the troublesome bacteria. Once the food is infected, the resistance of these bacteria to freezing means consumers are at risk of infection.
The Danger of Listeria

As mentioned, freezing food or storing it in cold temperatures — the usual trusty approach to eliminate bacteria-related issues from food — have no effect on listeria.
Colder temperatures typically help with food preservation and protection by killing bacteria. Far from being killed, Listeria monocytogenes can not only survive but potentially grow in refrigerated conditions or other food preservation environments.
How to Tell if Food Has Listeria
You might think you can tell if food has Listeria if it looks or smells funny, but that isn’t the case. The food will still look and smell the same, even with Listeria bacteria.
In some cases, it can take up to 70 days for Listeria symptoms to appear, so it is recommended that anyone who has consumed the product continue to monitor themselves and seek medical advice if necessary.
How to Kill Listeria
Listeria tends to multiply when stored in cold temperatures, so the best way to kill the bacteria is to make the food hot. This means pasteurizing and thoroughly cooking the food until it is piping hot.
This is supposed to be the best way of preventing infection, but it isn’t guaranteed to work. For example, soft cheeses made from pasteurized milk have been known to be the source of Listeria outbreaks in the past.
No Illnesses Reported

The good news is that no illnesses have been reported at the time of writing, but customers have been warned of some signs and symptoms to look out for should they be worried about becoming infected.
Most healthy individuals may only have short-term symptoms, such as high fever, severe headaches, stiffness, nausea, abdominal pain and diarrhea. Pregnant women, in particular, should stay away from the cheese, as the bacteria could cause them to have a miscarriage or stillbirth.
How People Get Sick From Listeria

People can become ill by eating food contaminated with these Listeria monocytogenes. If exposed to the bacteria in this way, they develop a disease known as listeriosis.
Those infected can begin to see symptoms within a few hours, or it can take several days after consuming the contaminated food. The longer contaminated food is left and stored in the refrigerator, the greater the risk as the more opportunity the bacteria has to grow.
Production Has Been Suspended

Due to a recall being required, Kenny’s Farmhouse Cheese has halted production of its St. Jerome cheese until it has worked with the FDA to investigate the matter.
The company hopes that production will begin again soon but wants to ensure that no one becomes infected by any of its products.
How the FDA Classifies Outbreaks

The FDA has three levels of classification for outbreaks like this that indicate the potential health hazard that the product targeted for recall poses to members of the pubic.
These three levels of hazard classification are assigned a numerical designation of I, II and III. Risk increases as the numerical classification decreases.
Class III

A Class III recall is the lowest level of risk assigned by the FDA, Class II is more serious than a Class III, and Class I is more serious than this — the most serious situation, in fact.
A Class III recall describes a situation where the FDA initiates a recall of products it believes are unlikely to cause “adverse health consequences.”
Class II

A Class II recall of a product means the FDA has identified a risk to the health of members of the public should they come into contact with the product.
Specifically, Class II describes “a situation in which use of, or exposure to, a violative product may cause temporary or medically reversible adverse health consequences or where the probability of serious adverse health consequences is remote.”
Highest Risk Classification

While conducting its investigation, the FDA had to raise the cheese’s risk level to the highest risk classification. This is known as a Class I recall — the most severe recall level any food item or company can be given.
Class I recalls are only given when a product is considered to have a high probability of causing “adverse health consequences or death.”
Voluntary Recall

Even though it has been put under the highest risk classification, the cheese is currently classed as a voluntary recall, as opposed to a mandatory one.
Around 130 pounds of St. Jerome Cheese have been recalled so far, with many more expected to be recalled as the word continues to spread.
The Cheese Was Sold in Several States

Despite being based in Kentucky, Kenny’s Farmhouse Cheese products are sold in various states across the U.S. This particular product was sold in Alabama, Georgia, Idaho, Indiana, Kentucky, North Carolina and Tennessee.
However, as they also sell products online, it’s likely that anyone could have purchased the recalled cheese. This is why people across the U.S. are being asked to return this product or throw it away if they have purchased it.
Previous Listeria Recalls

This is far from the first time the FDA has issued a recall for products believed to be at risk of contamination with Listeria monocytogenes.
In May, the FDA initiated a voluntary recall of the breakfast potato product “Broccoli Cheddar Breakfast Potato Bakes,” a product offered by the Veggies Made Great brand.
A Less Serious Recall

This recall was again due to the risk of listeria, though the FDA did not deem it as severe a risk as that posed by St. Gerome Cheese.
The FDA did not initially classify the voluntary recall of these potato products. Eventually, the FDA updated the recall notice of the some 10,544 boxes of the potato bake products to a Class II.
A Western Operation

These recalled potato products weren’t sold extensively across every state in the country. Instead, the recall only appeared to affect a handful of western U.S. states.
The potentially contaminated potato products were sent to distribution centers in Colorado, California and Arizona. From there, they were further distributed to stores in these same states, as well as stores in New Mexico, Nevada and Utah.
The Classic Delight Recall

Prior to this recall of potato products, other companies had announced product recalls due to fears of contamination with Listeria monocytogenes.
St. Mary’s, OH-based Classic Delight LLC saw a recall notice put in place for individually wrapped sandwiches it produced due to the potential presence of the disease-causing bacteria.
Overseas Listeria Recalls

Product recalls due to potential Listeria contamination have made headlines a lot around the world recently, as it’s not an issue exclusive to the U.S.
The UK’s FDA equivalent, the Food Standards Agency (FSA), initiated a recall of 101 ready-to-eat food products like sandwiches, salads and paninis due to possible listeria contamination. This potential outbreak was particularly concerning because the products were supplied to retail stores in healthcare settings.
What Should You Do if You Purchased the Recalled Cheese?

If you have purchased the St. Jerome cheese, you should not consume it and should either return it to your point of purchase or dispose of it. If you have consumed any of it, look for signs of infection and seek medical treatment if necessary.
It’s important to note that the St. Jerome cheese is the only known product from Kenny’s Farmhouse Cheese that is believed to be contaminated with Listeria. All other products are considered safe, but you should still notify a medical professional if you consume any food items and become very unwell.
